Artificial intelligence-driven forex trading software is gaining broader adoption across retail and institutional markets as financial firms integrate automation into currency trading operations. The technology combines machine learning models, algorithmic execution, and real-time data analysis to support faster trade decision frameworks. The shift reflects wider digitization trends in financial services and increasing reliance on automated infrastructure for high-volume market activity.
Growth of AI-Driven Automation in Currency Markets
AI forex trading software refers to platforms that use statistical models and adaptive algorithms to analyze price data, volatility patterns, and market signals without manual execution. These systems operate within predefined parameters while continuously refining trade strategies using historical and live data inputs.
Automation in forex trading is not new. Algorithmic trading has existed for decades in institutional markets. The difference lies in the use of advanced machine learning methods that allow software to detect non-linear patterns and react to market conditions dynamically.
Key drivers behind adoption include:
Increased market data availability
Faster computing infrastructure
Demand for 24-hour automated execution
Reduced latency in order processing
Scalable trading operations
Core Technologies Behind AI Forex Software

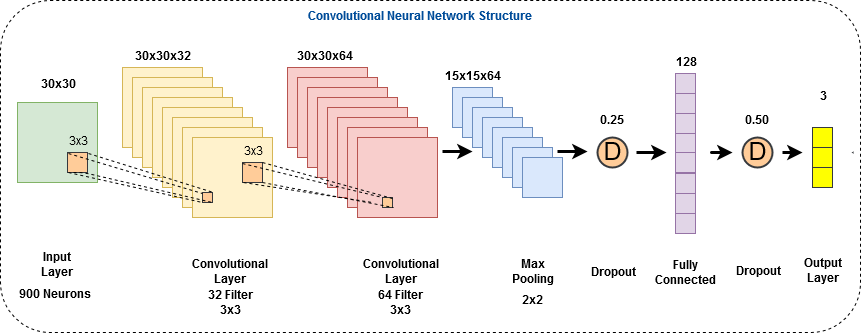

AI trading platforms rely on a layered technology structure combining data science and financial engineering.
Machine Learning Models
Supervised and unsupervised learning models analyze historical price behavior, liquidity shifts, and macroeconomic correlations. These models attempt to identify statistical patterns that may not be visible through traditional technical analysis.
Natural Language Processing
Some advanced platforms incorporate news sentiment analysis. Natural language processing engines scan financial headlines and economic reports to evaluate potential market impact in real time.
Predictive Analytics Infrastructure
Predictive engines process large datasets across multiple timeframes. These systems operate on distributed cloud architecture to maintain performance under high data loads.
Operational Structure of AI Forex Trading Systems
AI trading software typically operates through structured modules that separate analysis, decision logic, and execution.
| Component | Function | Role in Trading Workflow |
|---|---|---|
| Data Engine | Collects live and historical price feeds | Market input processing |
| Model Layer | Applies statistical learning models | Signal generation |
| Risk Module | Enforces position limits and exposure rules | Capital protection |
| Execution Layer | Sends automated trade orders | Market access |
| Monitoring System | Tracks performance metrics | System stability |
This modular architecture allows firms to update individual components without disrupting entire systems.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Automated trading systems operate under financial regulations that vary by jurisdiction. Many regulatory frameworks focus on risk transparency, system testing, and audit trails.
Regulators generally require:
Clear documentation of algorithm behavior
Risk management safeguards
Logging of automated decisions
Market abuse prevention controls
Institutional participants often subject AI models to stress testing to evaluate behavior during extreme volatility conditions.
Market Impact and Industry Response
The rise of AI-based forex platforms has influenced both liquidity distribution and competition in currency markets. High-speed automation increases order frequency and execution precision, which can compress spreads and alter short-term price behavior.
Financial institutions increasingly invest in proprietary algorithmic infrastructure. At the same time, retail trading platforms now offer simplified AI tools integrated into consumer-facing applications. This dual-track development reflects broader democratization of financial technology.
Infrastructure Requirements and Limitations


Despite rapid growth, AI forex systems require significant technical infrastructure.
Common operational requirements include:
Low-latency data connections
High-performance computing capacity
Secure cloud architecture
Continuous system monitoring
Model retraining pipelines
Limitations remain in areas such as overfitting risk, model transparency, and sensitivity to unexpected market shocks. Automated systems depend heavily on data quality and system uptime.
Institutional Versus Retail Adoption
Institutional firms tend to deploy custom-built AI frameworks integrated with proprietary liquidity networks. Retail platforms often rely on packaged algorithmic tools designed for accessibility rather than deep customization.
Differences between adoption environments include:
| Factor | Institutional Use | Retail Use |
|---|---|---|
| Customization Level | High | Limited |
| Infrastructure Control | Direct ownership | Platform-managed |
| Capital Scale | Large portfolios | Individual accounts |
| Compliance Oversight | Extensive | Platform-based safeguards |
These structural differences shape how AI trading tools function across market segments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What defines AI forex trading software?
AI forex trading software uses machine learning algorithms and automated execution engines to analyze currency markets and place trades without manual intervention.
How does AI differ from traditional algorithmic trading?
Traditional algorithmic trading follows fixed rule-based logic, while AI systems adapt models based on new data and statistical learning processes.
Are AI trading systems fully autonomous?
Most systems operate within predefined risk frameworks and require monitoring infrastructure. Autonomy is constrained by compliance and capital controls.
Do regulators oversee automated forex trading?
Yes. Many jurisdictions impose reporting, transparency, and risk management requirements on automated trading operations.
Final Verdict
AI forex trading software represents an expansion of automation within currency markets through machine learning, predictive analytics, and structured execution systems. Adoption spans institutional and retail environments, supported by evolving infrastructure and regulatory oversight. The technology reflects broader financial sector digitization while operating within established compliance frameworks.



Post a Comment