Scalping in the foreign exchange market depends heavily on execution speed, pricing structure, and platform stability. Broker infrastructure plays a measurable role in trade outcomes because scalping strategies rely on small price movements executed repeatedly. Regulatory oversight, spreads, order routing, and latency therefore carry operational significance. Understanding how brokers structure their trading environments provides context for evaluating suitability for scalping activity.
What Defines a Scalping-Compatible Forex Broker
A broker suitable for scalping is primarily defined by measurable infrastructure characteristics rather than marketing positioning. These characteristics determine whether short-duration trades can be executed consistently under live market conditions.
Execution Infrastructure
Execution quality is influenced by server location, order routing technology, and liquidity access. Brokers using direct market access or aggregated liquidity pools generally provide faster fills and reduced slippage during high-volume sessions.
Key infrastructure factors include:
Average execution latency
Slippage control mechanisms
Server proximity to major liquidity hubs
Order matching efficiency
Spread and Commission Structure
Scalping strategies are highly sensitive to transaction costs. Even fractional differences in spread or commission rates can materially alter net performance.
Important cost components:
Raw spread availability
Commission per lot
Swap exposure for short holds
Hidden execution markups
Trading Platform Stability
Platform reliability becomes critical when trade frequency is high. Interruptions or platform lag directly affect order timing.
Common platform features used by scalpers:
One-click trading
Advanced order types
Low-latency bridge integration
Stable mobile and desktop synchronization
Brokers Commonly Associated With Scalping Conditions
The following brokers are frequently evaluated based on execution transparency, pricing models, and infrastructure designed for active trading. The comparison reflects operational structure rather than promotional ranking.
| Broker | Execution Model | Average EUR/USD Spread | Commission Model | Platform Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC Markets | ECN-style routing | Low raw spread | Commission-based | MT4, MT5, cTrader |
| Pepperstone | No dealing desk | Tight variable | Commission-based | MT4, MT5, cTrader |
| FP Markets | Direct liquidity access | Raw spread | Commission-based | MT4, MT5, IRESS |
| Tickmill | ECN infrastructure | Low spread | Fixed commission | MT4, MT5 |
These brokers operate under regulatory frameworks that require order transparency and client fund segregation, which affects operational reliability.
Regulatory Oversight and Operational Transparency
Scalping activity increases trade volume, which makes dispute resolution frameworks and regulatory supervision relevant. Oversight bodies impose requirements on:
Capital adequacy
Client fund protection
Execution reporting
Complaint handling
Jurisdictional regulation does not determine profitability but contributes to structural reliability.
Liquidity Access and Market Depth
Scalping depends on the ability to enter and exit positions without excessive price impact. Brokers connected to tier-one liquidity providers generally show deeper order books during peak sessions.
Market depth affects:
Spread stability during volatility
Slippage during news events
Fill consistency in rapid sequences
Institutional-style liquidity aggregation is often associated with brokers positioned toward professional trading environments.
Platform Tools Used in Scalping Workflows
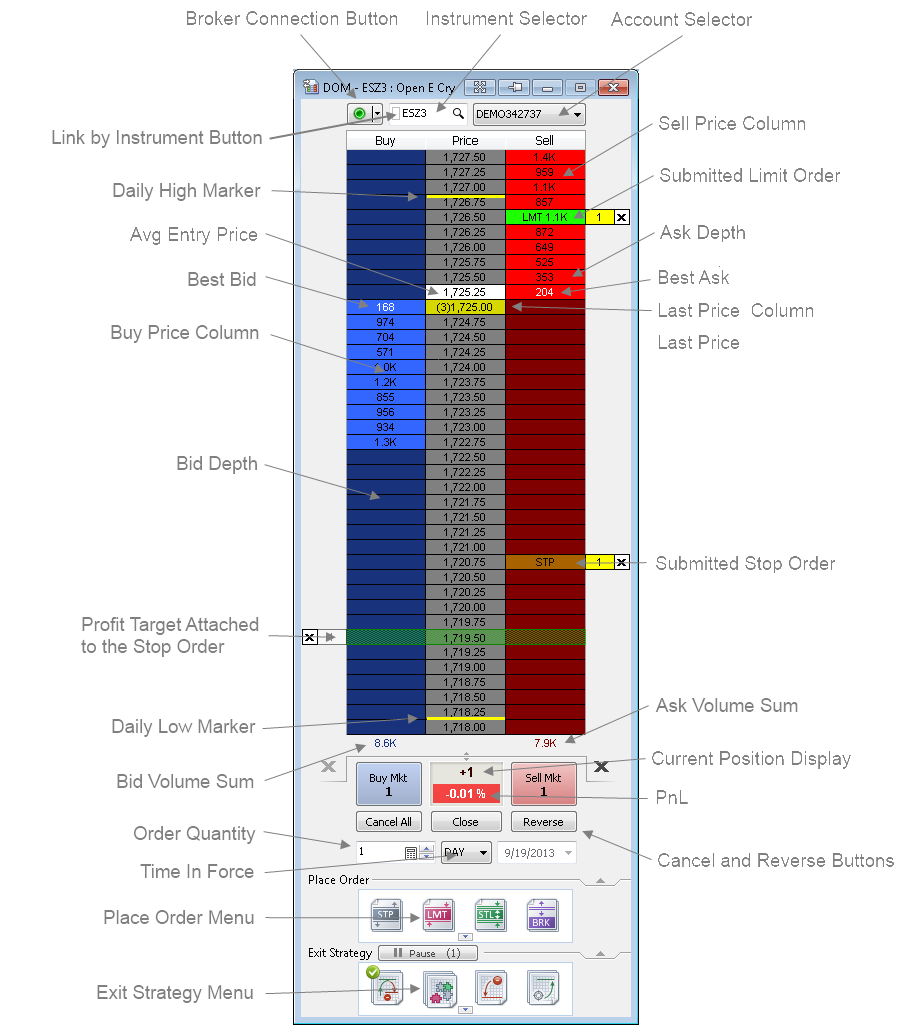

Scalpers typically rely on technical platform features designed for rapid execution and order precision.
Commonly used tools include:
Depth of market display
Hotkey execution
Tick chart monitoring
Automated trade scripting
VPS integration for latency reduction
Platform architecture affects response time under heavy order flow conditions.
Risk Controls and Broker Trade Policies
Broker policies toward scalping vary. Some dealing desk brokers restrict ultra-short trades due to internal risk management structures. Brokers advertising unrestricted scalping usually operate market execution environments without minimum holding periods.
Policy transparency matters in areas such as:
Stop level restrictions
Order distance rules
Trade frequency limits
Hedging permissions
Clear policy documentation reduces operational uncertainty.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes scalping different from standard forex trading
Scalping focuses on capturing small price changes repeatedly over short time frames. Trade duration can range from seconds to minutes, requiring rapid execution and low transaction costs.
Do all brokers allow scalping
Not all brokers support unrestricted scalping. Some impose execution limits or internal dealing rules that discourage very short holding periods.
Why spreads matter more in scalping
Scalping targets narrow price movements. Transaction costs consume a larger percentage of potential gains compared to longer-term trading.
Is commission-based pricing better for scalpers
Commission models paired with raw spreads often produce lower total trading costs for high-frequency strategies, depending on execution quality.
Final Verdict
Broker suitability for scalping is determined by execution speed, cost structure, platform stability, and regulatory transparency. Infrastructure design, liquidity access, and operational policy clarity collectively influence whether a broker environment supports high-frequency trading conditions without structural friction.


Post a Comment