Professional traders use structured trade journals to document decisions, outcomes, and risk exposure, creating a measurable record of trading activity. This process matters because consistent documentation supports performance evaluation, compliance discipline, and behavioral analysis. Trade journaling has become a standardized practice across institutional and independent trading environments, particularly as markets generate increasing volumes of data.
What a Trade Journal Records
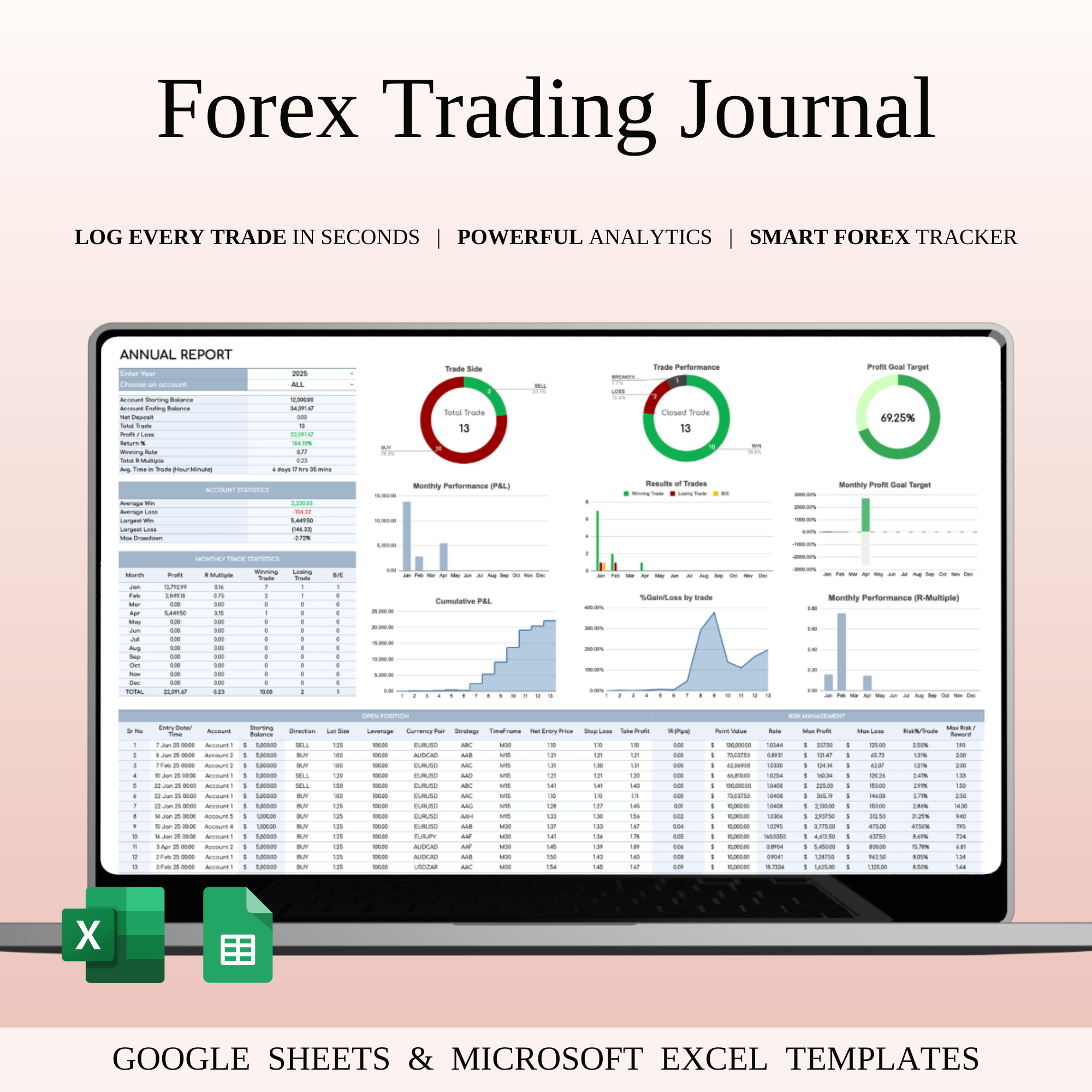


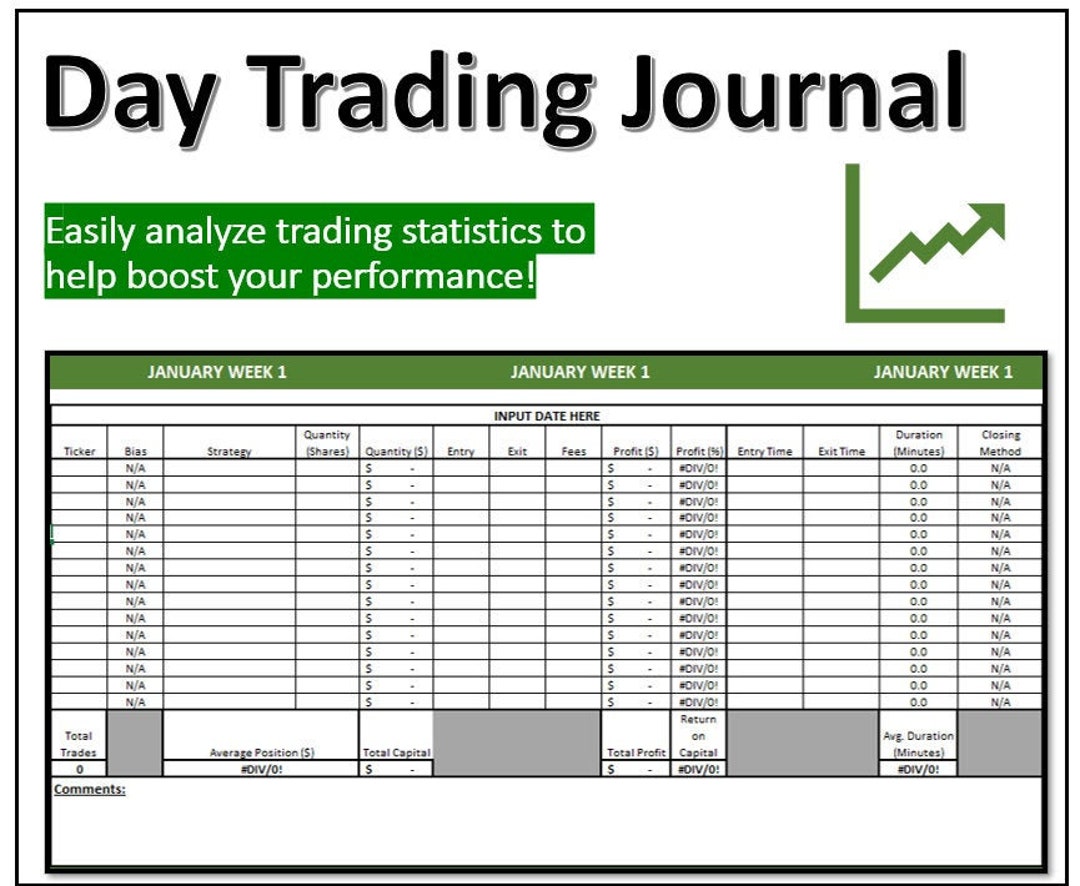
A professional trade journal is a systematic log rather than a diary. It captures quantitative and qualitative information for each executed position. The goal is to build a structured dataset that can be reviewed objectively.
Typical journal fields include:
| Category | Data Recorded |
|---|---|
| Trade identification | Date, time, asset, market session |
| Entry details | Entry price, position size, order type |
| Exit details | Exit price, stop loss, take profit |
| Risk metrics | Risk per trade, account exposure |
| Strategy tags | Setup classification, market condition |
| Execution notes | Reason for entry and exit |
| Outcome metrics | Profit and loss, risk-to-reward ratio |
These fields allow traders to evaluate performance across strategies, timeframes, and market environments.
Structured Formats Used by Professional Traders
Professional traders often use standardized formats designed to support statistical review.
Spreadsheet-Based Logs
Spreadsheets remain widely used because they allow filtering, sorting, and formula-based performance tracking. Institutional traders frequently integrate automated trade exports from brokerage platforms.
Key advantages include:
- Consistent numerical tracking
- Easy statistical aggregation
- Compatibility with reporting tools
Dedicated Journaling Software

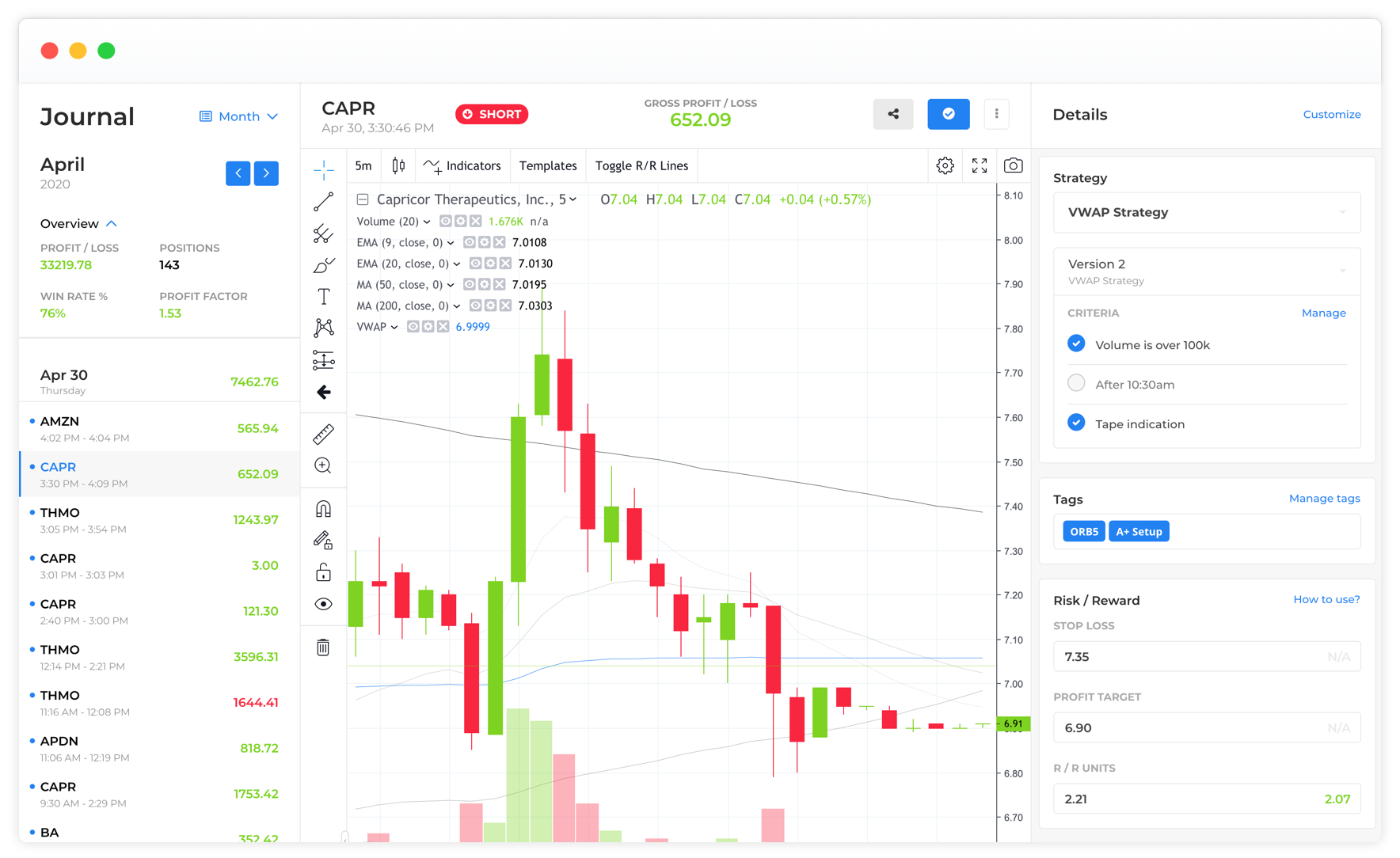

Specialized journaling platforms expand on spreadsheets by adding analytics layers. These systems categorize trades automatically and generate visual reports.
Common features include:
- Equity curve visualization
- Drawdown tracking
- Strategy performance segmentation
- Behavioral pattern detection
Such tools are frequently used by proprietary trading firms and algorithmic traders.
Written Execution Logs
Some discretionary traders maintain handwritten execution notes alongside digital records. These notes document psychological conditions, market context, and discipline adherence. The written component serves as a behavioral audit trail.
Metrics Professional Traders Analyze
Trade journaling supports structured performance measurement. Instead of focusing on individual wins or losses, professionals analyze aggregated data.
Core metrics include:
| Metric | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Win rate | Measures consistency of strategy |
| Average risk-to-reward | Evaluates trade efficiency |
| Expectancy | Long-term profitability indicator |
| Maximum drawdown | Capital protection assessment |
| Trade frequency | Exposure and discipline tracking |
These metrics transform raw trade history into quantifiable performance indicators.
Behavioral Documentation and Discipline Tracking



Professional journals also record decision discipline. Behavioral entries may include:
- Adherence to predefined strategy
- Emotional state during execution
- Deviations from risk management rules
- Market conditions influencing judgment
This documentation helps identify recurring behavioral patterns that impact performance.
Regulatory and Institutional Context
Trade journaling is aligned with risk governance practices used in institutional finance. Firms often require traders to maintain audit trails that document rationale and execution details. Structured records support compliance reviews and internal performance assessments.
In regulated environments, journaling contributes to transparency, accountability, and post-trade evaluation frameworks.
Historical Influence on Trade Documentation
The concept of documenting trades has long existed in professional markets. Early market operators such as Jesse Livermore emphasized record keeping as a method for studying patterns and avoiding repeated errors. Modern journaling systems extend this principle through digital analytics.
FAQ
Why do professional traders journal every trade?
Trade journaling creates a measurable performance record. It allows objective review of strategies, execution quality, and risk management.
What distinguishes professional journals from casual notes?
Professional journals use standardized data fields that enable statistical analysis. Casual notes typically lack structured metrics and consistency.
Are journals used only for losing trades?
Professional records include all trades. Complete datasets are required for accurate expectancy and drawdown calculations.
Do institutions require journaling?
Many institutional trading environments require documentation to support compliance audits and performance reporting.
Final Verdict
Professional trade journaling is a structured documentation process that records execution details, risk exposure, and behavioral observations. The practice converts individual trades into analyzable datasets, supporting performance evaluation and institutional accountability. Consistent journaling remains a foundational element of professional trading operations.



Post a Comment